Introducing the list of 3G offenses in Texas, a legal framework that addresses a range of serious crimes. This guide delves into the intricacies of these offenses, exploring their definitions, punishments, and the factors that influence sentencing decisions. Prepare to navigate the complexities of Texas law as we uncover the consequences and defenses associated with 3G offenses.
Within the vast legal landscape, 3G offenses stand out as a category of severe criminal acts. Their impact extends beyond individual perpetrators, affecting society as a whole. This guide unravels the complexities of these offenses, providing a comprehensive understanding of their legal implications and the strategies employed in their defense.
Legal Classification of 3G Offenses in Texas
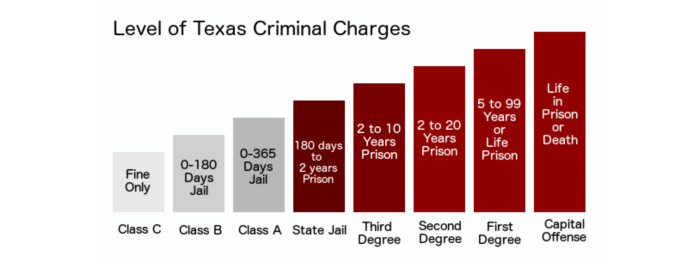
In Texas, 3G offenses refer to a specific category of felonies that involve the unlawful possession or use of a firearm by a convicted felon. These offenses are considered particularly serious and carry severe penalties.
The definition of a 3G offense is Artikeld in Section 46.04 of the Texas Penal Code. According to the statute, a person commits a 3G offense if they have previously been convicted of a felony and are subsequently found in possession of a firearm or if they use a firearm in the commission of a felony.
List of 3G Offenses and Punishments
The following is a list of 3G offenses and their corresponding punishments in Texas:
- Unlawful Possession of a Firearm by a Felon: This offense is punishable by a minimum of 5 years and a maximum of 99 years in prison.
- Use of a Firearm in the Commission of a Felony: This offense is punishable by a minimum of 10 years and a maximum of life in prison.
Factors that Determine the Severity of a 3G Offense
The severity of a 3G offense is determined by several factors, including:
- The nature of the underlying felony conviction
- Whether the offender used the firearm in the commission of a felony
- The offender’s criminal history
In general, 3G offenses are considered to be among the most serious felonies in Texas. The penalties for these offenses are severe, and they can have a significant impact on the offender’s life.
Sentencing Guidelines for 3G Offenses

Sentencing for 3G offenses in Texas is guided by a set of guidelines established by the Texas Legislature. These guidelines provide a range of possible sentences for each type of 3G offense, taking into account the severity of the offense and the offender’s criminal history.
Sentencing Ranges
- Class A Misdemeanor:Up to one year in jail and/or a fine of up to $4,000.
- Class B Misdemeanor:Up to 180 days in jail and/or a fine of up to $2,000.
- Class C Misdemeanor:Up to 90 days in jail and/or a fine of up to $500.
Factors Affecting Sentencing Decisions
In addition to the type of offense, several other factors can affect sentencing decisions, including:
- Prior criminal record:Offenders with a history of prior convictions may receive harsher sentences.
- Mitigating circumstances:Factors such as remorse, cooperation with law enforcement, and mental health issues may be considered in sentencing.
- Aggravating circumstances:Factors such as the use of a weapon, causing serious bodily injury, or committing the offense while on probation or parole may result in a harsher sentence.
Potential Consequences of a 3G Offense Conviction, List of 3g offenses in texas
A conviction for a 3G offense can have significant consequences, including:
- Jail time:Depending on the severity of the offense and the offender’s criminal history, a conviction for a 3G offense may result in a jail sentence of up to one year.
- Fines:Fines for 3G offenses can range from $500 to $4,000.
- Loss of driving privileges:A conviction for a 3G offense that involves driving while intoxicated or reckless driving may result in the loss of driving privileges.
- Probation:Offenders convicted of a 3G offense may be placed on probation, which requires them to meet certain conditions, such as attending counseling or avoiding alcohol or drugs.
Legal Defenses for 3G Offenses

When facing a 3G offense charge, it’s crucial to understand the available legal defenses to protect your rights. These defenses aim to challenge the prosecution’s case by casting doubt on the elements of the offense or presenting mitigating circumstances.
Building a strong defense involves a thorough understanding of the elements of the offense, identifying potential weaknesses in the prosecution’s case, and developing a strategy that effectively addresses those weaknesses.
Entrapment
- Entrapment occurs when law enforcement officials induce or coerce a person into committing a crime they would not have otherwise committed.
- To establish entrapment, the defense must prove that the defendant was not predisposed to commit the crime and that the law enforcement officials’ conduct was outrageous.
Lack of Criminal Intent
- Criminal intent, also known as mens rea, is an essential element of most crimes.
- The defense of lack of criminal intent argues that the defendant did not have the necessary mental state, such as intent, knowledge, or recklessness, to commit the offense.
Self-Defense or Defense of Others
- Self-defense or defense of others is a justification defense that allows a person to use reasonable force to protect themselves or another person from imminent harm.
- To establish self-defense, the defendant must show that they reasonably believed they were in imminent danger and that the force they used was necessary to protect themselves or others.
Insanity
- Insanity is a defense that argues that the defendant was mentally ill at the time of the offense and unable to appreciate the nature and consequences of their actions.
- To establish insanity, the defense must prove that the defendant suffered from a severe mental illness that prevented them from understanding the wrongfulness of their actions.
Impact of 3G Offenses on Individuals and Society

3G offenses can have devastating consequences for individuals and society as a whole. They can lead to significant social and economic problems, and can have a profound impact on victims and their families.
One of the most significant social consequences of 3G offenses is the erosion of trust within communities. When people feel unsafe in their own homes and neighborhoods, it can lead to a breakdown in social cohesion and a decline in civic engagement.
This can have a ripple effect, leading to other social problems such as increased crime and poverty.
Economic Consequences
3G offenses can also have a significant economic impact on individuals and society. Victims of 3G offenses may lose income due to missed work or medical expenses. They may also experience long-term psychological and emotional trauma, which can make it difficult to return to work or maintain relationships.
Looking into 3G offenses in Texas can be quite the journey, much like the adventures of a young cub pilot navigating the mighty Mississippi River, as described in Cub Pilot on the Mississippi . Just as the cub pilot faced various challenges, understanding 3G offenses in Texas requires careful examination of the legal landscape.
In addition to the costs to victims, 3G offenses can also impose significant costs on society as a whole. These costs include the cost of law enforcement, prosecution, and incarceration. They also include the cost of providing medical and mental health services to victims and their families.
Impact on Victims and Families
The impact of 3G offenses on victims and their families can be profound. Victims may experience physical injuries, emotional trauma, and financial losses. They may also be at risk of retaliation from the offender.
Family members of victims may also experience significant trauma. They may worry about the victim’s safety and well-being, and they may feel helpless to protect them. They may also experience financial difficulties if the victim is unable to work or if they have to pay for medical expenses.
Rehabilitation and Reintegration Programs
Rehabilitation and reintegration programs play an important role in reducing the recidivism rate among individuals convicted of 3G offenses. These programs provide offenders with the skills and support they need to successfully reintegrate into society.
Rehabilitation programs typically include cognitive-behavioral therapy, substance abuse treatment, and job training. Reintegration programs provide offenders with housing, employment, and other support services.
Research has shown that rehabilitation and reintegration programs can be effective in reducing recidivism. One study found that offenders who participated in a cognitive-behavioral therapy program were 43% less likely to be rearrested than offenders who did not participate in the program.
Current Legal Trends and Developments in 3G Offenses

Recent years have witnessed a surge in the prosecution of 3G offenses, prompting legislative and judicial responses. Notably, several states have enacted stricter penalties for 3G offenses, reflecting a growing societal intolerance for such behavior.
Emerging Legal Issues and Challenges
One emerging legal issue is the intersection of 3G offenses with other criminal statutes, such as hate crime laws. Courts are grappling with how to apply hate crime enhancements to 3G offenses, considering factors such as the victim’s perceived race, religion, or sexual orientation.Another
challenge arises from the use of social media in perpetrating 3G offenses. The anonymity and reach of online platforms present unique difficulties in identifying and prosecuting offenders.
Potential Future Developments
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see new forms of 3G offenses emerge. Prosecutors and defense attorneys alike must stay abreast of these developments to ensure that the law keeps pace with the changing landscape of 3G offenses.
Clarifying Questions: List Of 3g Offenses In Texas
What constitutes a 3G offense in Texas?
3G offenses in Texas are serious crimes that fall within a specific category of felony offenses.
What are the potential penalties for a 3G offense conviction?
Penalties vary depending on the specific offense, but generally include imprisonment for a minimum of 5 years and a maximum of 99 years or life.
Are there any common defenses to 3G offense charges?
Yes, common defenses include lack of intent, self-defense, and insufficient evidence.