Label the tonicity for each solution – Labeling the tonicity of solutions is a crucial aspect of understanding the behavior of biological systems. Tonicity refers to the relative concentration of solutes in a solution compared to another solution, and it plays a significant role in various biological processes.
This article provides an overview of tonicity, methods for labeling it, and its applications in different fields.
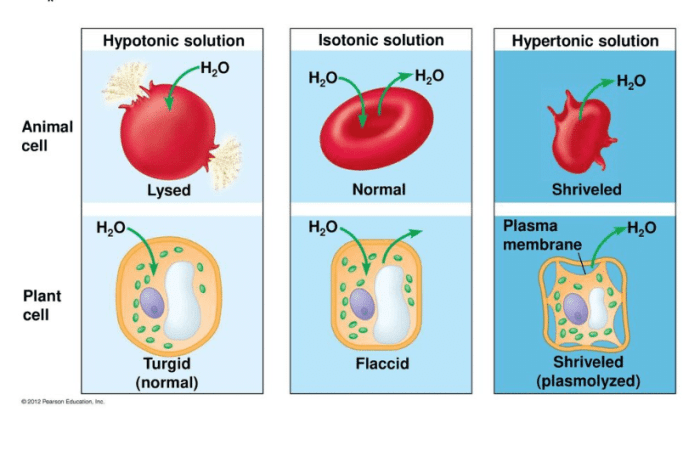
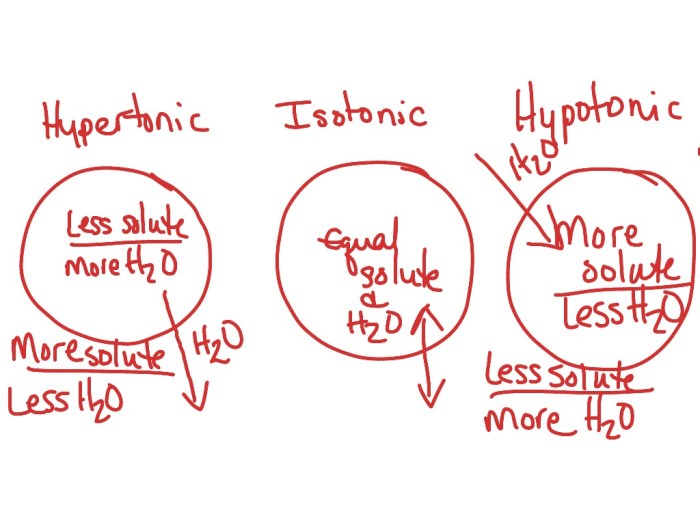
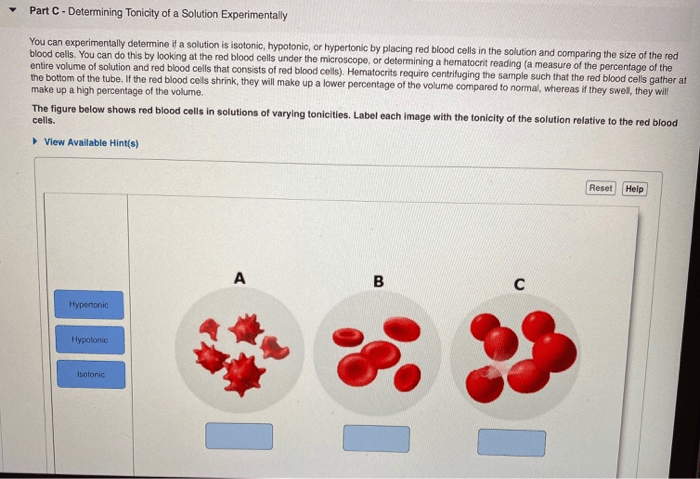
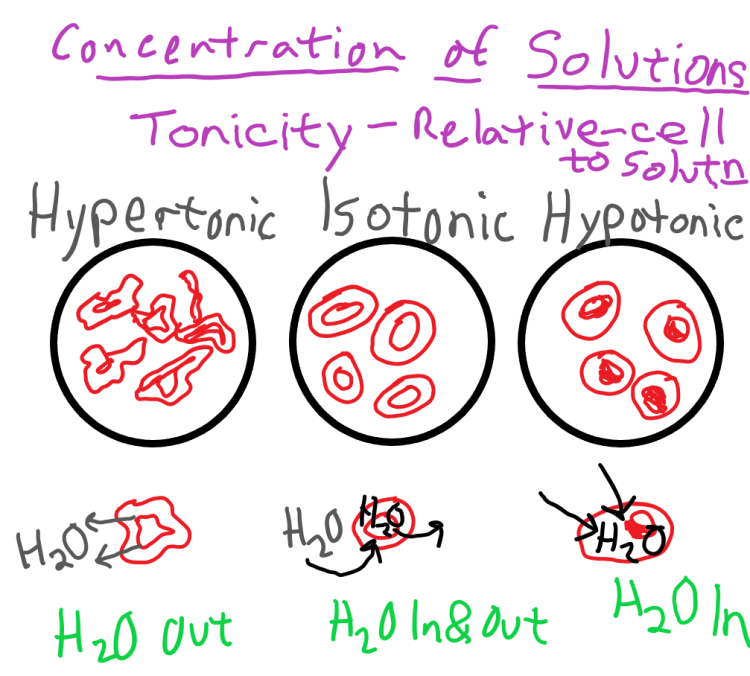
Tonicity can be classified into three types: isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic. Isotonic solutions have the same concentration of solutes as the reference solution, hypotonic solutions have a lower concentration, and hypertonic solutions have a higher concentration.
Introduction

Tonicity refers to the relative concentration of solutes in a solution compared to another solution, particularly in biological systems. It plays a crucial role in maintaining cell volume and function, as well as in various physiological processes.
Tonicity is classified into three main types:
Isotonic Solutions
- Have the same solute concentration as the reference solution.
- Do not cause a net movement of water across the cell membrane.
- Maintain cell volume and shape.
Hypotonic Solutions
- Have a lower solute concentration than the reference solution.
- Cause water to move into the cell, potentially leading to cell swelling or lysis.
- Can be used to promote cell growth and expansion.
Hypertonic Solutions
- Have a higher solute concentration than the reference solution.
- Cause water to move out of the cell, leading to cell shrinkage or crenation.
- Can be used to preserve cells or tissues.
Methods for Labeling Tonicity
Determining the tonicity of a solution is crucial in various scientific and medical fields. It involves understanding the principles of osmosis and employing appropriate techniques to measure the solution’s ability to cause water movement across a semipermeable membrane.
Osmosis and Tonicity
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration through a semipermeable membrane. Tonicity refers to the ability of a solution to cause osmosis. Solutions can be classified as isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic, depending on their tonicity relative to another solution.
Osmometers and Tonicity Measurement
Osmometers are devices used to measure the tonicity of solutions. They employ semipermeable membranes to separate the solution from a reference solution with known tonicity. The movement of water across the membrane creates a pressure difference, which is measured and used to determine the solution’s tonicity.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Labeling Tonicity
- Prepare two solutions with different solute concentrations.
- Set up an osmometer with a semipermeable membrane separating the two solutions.
- Observe the direction of water movement across the membrane.
- Based on the water movement, label the solutions as isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic:
- Isotonic: No net water movement, solutions have equal tonicity.
- Hypotonic: Water moves into the solution, the solution has lower tonicity than the reference.
- Hypertonic: Water moves out of the solution, the solution has higher tonicity than the reference.
Applications of Tonicity Labeling: Label The Tonicity For Each Solution
Tonicity labeling plays a pivotal role in various scientific disciplines, including medicine, biology, and environmental science. It enables researchers and practitioners to determine the osmotic pressure of solutions, which is crucial for understanding cellular processes, diagnosing and treating medical conditions, and monitoring environmental health.
In medicine, tonicity labeling is essential for administering fluids and medications intravenously. By matching the tonicity of the solution to that of the patient’s blood, healthcare professionals can prevent adverse effects such as hemolysis or cell shrinkage.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Medical Conditions
- Tonicity labeling aids in diagnosing conditions such as hypertonicity (high osmotic pressure) and hypotonicity (low osmotic pressure).
- It helps guide treatment decisions for conditions like dehydration and fluid overload, where restoring fluid balance is crucial.
Environmental Monitoring and Research
- Tonicity labeling is used in environmental monitoring to assess the salinity of water bodies.
- It helps researchers understand the impact of pollutants on aquatic ecosystems and monitor changes in water quality over time.
Case Studies and Examples
Tonicity labeling has been successfully employed in various real-world applications to enhance the understanding and management of solutions. Here are a few notable case studies:
-
Medical Diagnosis and Treatment, Label the tonicity for each solution
Tonicity labeling plays a crucial role in medical diagnostics and treatment. For instance, measuring the tonicity of body fluids can aid in diagnosing conditions like dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and kidney disorders. Additionally, tonicity labeling is essential for formulating intravenous fluids and medications to ensure proper hydration and drug delivery.
-
Agricultural Applications
In agriculture, tonicity labeling helps optimize crop growth and yield. By determining the tonicity of soil solutions, farmers can adjust irrigation practices to maintain optimal water and nutrient uptake by plants. This approach enhances crop productivity and reduces water wastage.
-
Industrial Processes
Tonicity labeling finds applications in various industrial processes. For example, in the food industry, tonicity measurements help control the texture and shelf life of products. In the pharmaceutical industry, tonicity labeling ensures the stability and efficacy of drug formulations.
-
Environmental Monitoring
Tonicity labeling can provide valuable insights into the health of aquatic ecosystems. By measuring the tonicity of water bodies, scientists can assess the impact of pollutants, climate change, and other environmental factors on aquatic organisms.
Benefits and Limitations of Tonicity Labeling Methods
Different tonicity labeling methods offer varying advantages and drawbacks:
-
Osmometry
Benefits:Accurate and reliable measurements; well-established technique.
Limitations:Requires specialized equipment; can be time-consuming.
-
Electrical Conductivity
Benefits:Fast and inexpensive; portable equipment available.
Limitations:Influenced by the presence of ions; requires calibration for different solutions.
-
Vapor Pressure Osmometry
Benefits:Highly sensitive; suitable for small sample volumes.
Limitations:Requires specialized equipment; can be affected by volatile compounds.
-
Freezing Point Depression
Benefits:Simple and inexpensive; widely accessible equipment.
Limitations:Less accurate than other methods; requires precise temperature control.
The choice of tonicity labeling method depends on factors such as the desired accuracy, sample availability, and cost considerations.
FAQ Overview
What is the principle behind osmosis?
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
How is tonicity measured?
Tonicity can be measured using osmometers or other techniques that measure the osmotic pressure of a solution.
What are the applications of tonicity labeling in medicine?
Tonicity labeling is used in medicine to diagnose and treat conditions such as dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and kidney disease.